Why Keynes’ Economic Theories Failed In Reality
Authored by Lance Roberts via RealInvestmentAdvice.com,
A recent post from Daniel Lacalle, “How Keynesians Got The US Economy Wrong Again,” exposed the widening gap between John Maynard Keynes’ economic theory and reality. Despite the confident forecasts of leading Keynesian economists, the U.S. economy in 2025 continues to defy expectations. The Federal Reserve’s tightening cycle failed to trigger the widely predicted “hard landing,” and growth has proven more resilient. Simultaneously, inflation remains somewhat sticky, but still declining, and the economy refuses to follow the neat, linear pathways that textbook models suggest.

This latest embarrassment for Keynes’ orthodoxy is part of a much larger story. The failures aren’t isolated miscalculations but the predictable result of a flawed framework that policymakers have clung to for decades. Keynesian economics didn’t just “get it wrong” in 2025, but has repeatedly failed to deliver on its promises for over forty years. And the consequences are becoming impossible to ignore.
At its core, Keynesian economics is deceptively simple. When demand for the private sector falls, the government should borrow and spend to fill the gap. The idea is that temporary fiscal stimulus injections will smooth business cycles, reduce unemployment, and quickly return the economy to full capacity.
But the key word here is temporary. John Maynard Keynes was clear: governments should run deficits during downturns and surpluses during expansions. The debt incurred to rescue the economy should be repaid once conditions normalize.
However, in practice, this discipline never materialized. Politicians discovered that voters liked stimulus but hated austerity. Since the 1970s, deficits have become a permanent feature of U.S. fiscal policy, regardless of the business cycle. The results are sobering: the U.S. national debt now exceeds 120% of GDP, entitlement programs are structurally underfunded, and each crisis requires larger interventions with diminishing economic benefits.
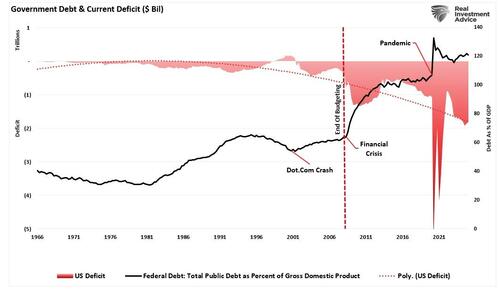
The COVID-19 pandemic was the ultimate Keynes experiment. Between 2020 and 2022, the federal government injected over $5 trillion in fiscal stimulus into the economy, complemented by the Federal Reserve slashing interest rates to zero and expanding its balance sheet by $120 billion each month. According to the Keynesian model, this unprecedented monetary and fiscal stimulus should have ushered in a durable economic boom.
The Failure of Artificial Growth
However, as we noted in “MMT Was Tried And Failed,” the massive flood of stimulus temporarily boosted economic growth by “pulling forward” future demand, but it also created several problems.
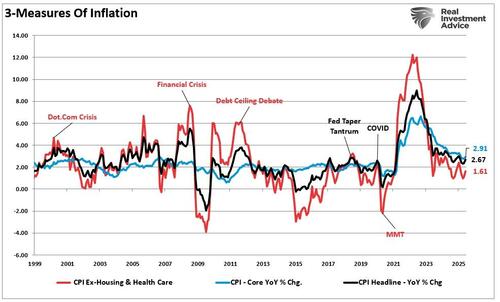
“The most obvious problem was the impact of dramatically increasing demand on a supply-stricken economy. With the economy “shut down” due to Government-mandated restrictions, the flood of stimulus payments led to a demand boost. Given the basic economics of supply versus demand, prices rose. As expected would be the case, the implementation led to a massive surge in inflation. (Given most Americans’ have fixed healthcare and housing payments for a contractual period, the third measure shows what cost-of-living is for most every month.)”
Crucially, inflation, excluding housing and healthcare, surged to nearly 12% during the pandemic-stimulus-infused spending spree. However, today, as the economy slows and the stimulus fades from the system, that inflation rate has declined to just 1.61%.
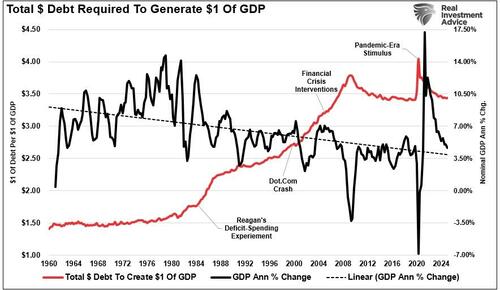
Secondly, the “economic boom” created by the demand-pull stimulus continues to disappear as the economy normalizes slowly back to roughly $3.50 in debt to make $1 of economic activity. Following the pandemic shutdown, the economy surged to unprecedented levels, nearing 17.5% nominal growth. On a shuttered economy, the byproduct of all that demand was an inflation surge to 40-year highs, peaking above 9% in 2022. Five years later, inflation continues to decline towards the Fed’s 2% target, but remains sticky as remnants of monetary and fiscal stimulus continue to flow through the system.
The Broken Transmission of Monetary Policy
A further failure of modern Keynesian policy is its overreliance on central banks. Through rate cuts and quantitative easing (QE), monetary stimulus has become the go-to solution for any economic slowdown. Yet the transmission mechanism between monetary policy and real economic activity has fundamentally broken. Artificial interventions and “MMT” failed to work in reality because the underlying transmission system failed.
“The promise of something for nothing will never lose its luster. So MMT should be viewed as a form of political propaganda rather than any real economic or public policy. And like all propaganda, we must fight it with appeals to reality. MMT, where deficits don’t matter, is an unreal place.”
Meanwhile, the velocity of money, the rate at which money changes hands in the economy, while recovering somewhat from the economic shutdown, continues to trend lower. In other words, the Fed can inject liquidity but fails to circulate productively. The velocity trend does not provide an encouraging outlook for GDP growth.
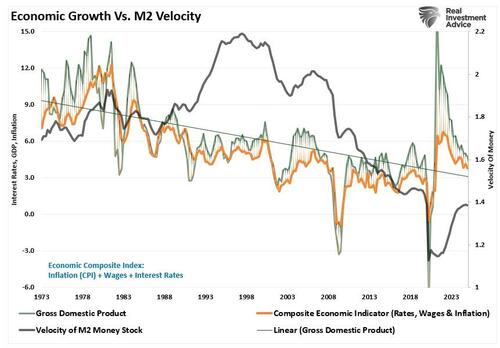
Given the weakening economic growth rates and subsequently declining inflation, a direct reflection of weakening consumer demand, banks have little incentive to expand lending at current rates, especially in an environment of tighter regulations and poor credit quality.
One key problem is that Keynesian models assume a linear cause-and-effect relationship between government spending and economic output. They focus almost entirely on aggregate demand, neglecting critical dynamics like debt saturation, supply chain fragilities, and the feedback loops of global capital markets.
In today’s highly financialized economy, government spending does not circulate efficiently. As noted, much of it gets trapped in financial markets, inflating asset prices rather than stimulating productive investment. Ultra-low interest rates, another hallmark of Keynesian policy, discourage savings and encourage debt-fueled speculation. This distorts capital allocation, causing malinvestment in unproductive assets like meme stocks, speculative real estate, and unprofitable tech ventures. Most benefits remain trapped in the top 10% of the economy, which owns roughly 88% of the inflation-adjusted financial assets.
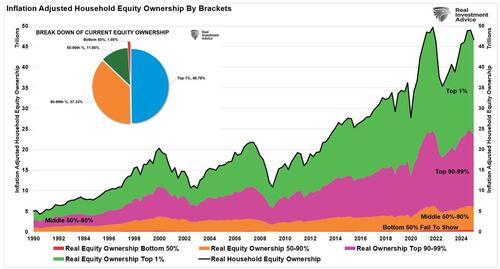
In other words, the wealthy retain the monetary injections while inflation taxes them away from the poor.
Mr. Lacallie highlighted this mismatch between Keynes’ theories and economic realities. As he noted, many mainstream economists repeatedly forecasted a 2023-2024 recession that never arrived, underestimated inflation persistence, and misread the impact of fiscal tightening. These forecasting errors expose deeper flaws in how Keynesians model the modern economy.
Hayek’s Warnings Prove Prophetic
The Austrian school of economics, particularly Friedrich Hayek’s views, starkly contrasts with Keynesian thinking. Austrian economists believe that a sustained period of low interest rates and excessive credit creation creates a dangerous imbalance between saving and investment. In other words, low interest rates tend to stimulate borrowing from the banking system, which leads, as one would expect, to the expansion of credit. This expansion of credit, then, in turn, increases the supply of money.
Therefore, as one would ultimately expect, the credit-sourced boom becomes unsustainable as artificially stimulated borrowing seeks out diminishing investment opportunities. Finally, the credit-sourced boom results in widespread malinvestments. When the exponential credit creation is no longer be sustainable, a “credit contraction” occurs, ultimately shrinking the money supply. The markets eventually “clear,” which causes resources to be reallocated towards more efficient uses.
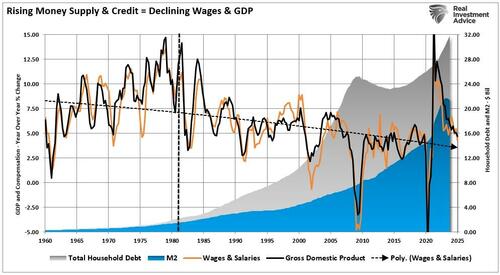
Modern policymakers refuse to allow this natural process. Each downturn results in more aggressive stimulus, which only delays the necessary corrections. The result has been a relentless build-up of economic imbalances. Inefficient businesses survive on cheap debt, zombie firms proliferate, and innovation suffers. Each economic expansion is weaker than the last, and each recovery depends on larger interventions to stay afloat.
Perhaps the greatest misconception perpetuated by Keynesian economists is that debt-financed stimulus is a free lunch. In reality, servicing the debt and rising debt service costs become a significant economic headwind. The Congressional Budget Office projects that U.S. interest payments will exceed national defense spending in the coming years and approach $1.5 trillion annually by 2030. Of course, that is assuming that rates stay where they are currently. The next crisis, which has become more common since the turn of the century, will significantly lower rates. As shown, a reduction in rates by 1% would dramatically impact future liabilities.
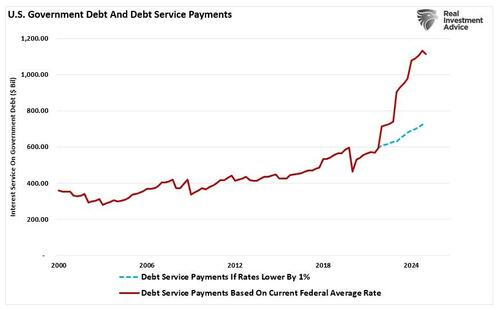
This is not just a fiscal issue—it’s a macroeconomic drag. Spending dollars on interest payments diverts them from infrastructure, education, or productive investment. Worse, rising debt levels crowd out private investment, distort capital markets, and reduce the flexibility to respond to future crises.
Conclusion: Keynes’ Economic Theory Has Failed
For the last 40 years, each Administration and the Federal Reserve have continued to operate under Keynes’s monetary and fiscal policies, believing the model worked. The reality, however, is that most of the economy’s aggregate growth is financed by deficit spending, credit expansion, and a reduction in savings.
This reduced productive investment and slowed the economy’s output. As the economy slowed and wages fell, the consumer took on more leverage, decreasing savings. The result of the increased leverage required more income to service the debt, rather than fuel increased consumption.
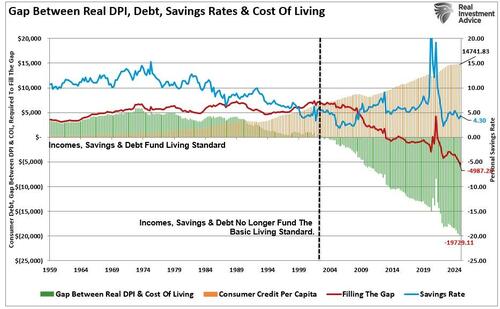
Secondly, most government spending programs redistribute income from workers to the unemployed. Keynes’ economists argue that this increases the welfare of many hurt by the recession. What their models ignore, however, is the reduced productivity that follows a shift of resources toward redistribution and away from productive investment.
All of these issues have weighed on the overall prosperity of the economy. What is most telling is the inability of current economists, who maintain our monetary and fiscal policies, to realize the problem of trying to “cure a debt problem with more debt.”
This is why Keynes’ economic policies have failed, from “cash for clunkers” to “Quantitative easing.” Each intervention either dragged future consumption forward or stimulated asset markets. Pulling future consumption forward leaves a “void” in the future that must be continually filled. However, creating an artificial wealth effect decreases savings, which could be used for productive investment.
It’s time we wake up and realize we are on the same path.
Tyler Durden
Fri, 09/05/2025 – 13:05









![Trwa udawana wojna o wolność słowa. Populiści nie zamierzają zmarnować takiej okazji. Straszą "autorytarnym reżimem cenzury" [OPINIA]](https://ocdn.eu/pulscms-transforms/1/O4Fk9kpTURBXy80YmZiMmRmZGQ4ODdhYWJmOTQzYmQyM2YxYzYwNjc0Zi5qcGeTlQMAzIzNEZTNCeOTCaYwNTk0NzcGkwXNBLDNAnbeAAGhMAE/donald-trump-prezydent-usa-i-brytyjski-polityk-nigel-farage-na-wiecu-w-arizonie-28-pazdziernika-2020-r.jpg)


